Just when we thought that schools couldn’t possibly absorb any more of society’s most complex needs being driven through their already heaving agendas, the crisis associated with the Coronavirus pandemic over the past 6 months suddenly focused a more harsh spotlight on the way in which increasing divisions between the haves and the have-nots determines outcomes for children and their families, not only in terms of academic achievement at school and beyond, but now in terms of health, employment and life-expectancy in the face of a global pandemic. Stark divisions which have already become entrenched during prolonged austerity, have become even more acute in the face of national lockdown measures, forcing many families into precarity they never imagined would touch them, and pushing the already vulnerable deeper into poverty which seems fitting for Victorian England, not 2020.
We have seen schools step up to the challenge without hesitation, sourcing food parcels for the families they serve, reinventing teaching through online lessons, providing devices and internet access for those that need it, producing work packs for home delivery where technology just isn’t going to be an option, rallying round and making sure that everyone is okay, learning, connected in one way or another to the school community. On the backdrop of so much activity, care, and action, the gross injustices of racial discrimination seemed to suddenly rear up into focus as well, as the brutal murder of George Floyd at the hands of police in the USA resonated with so many people worldwide, as a sign that enough is enough.
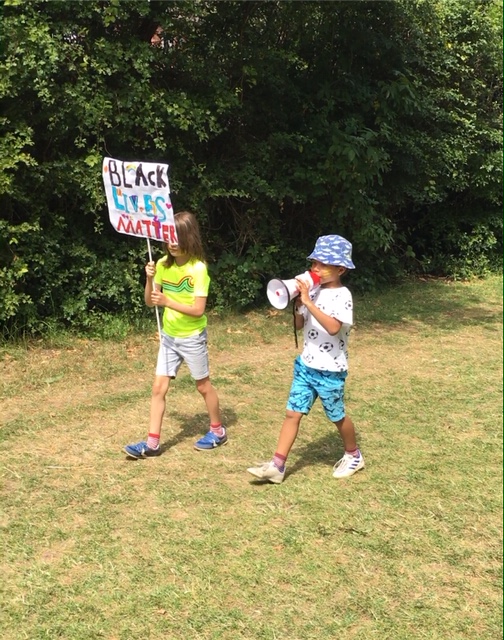
The grassroots organisation, The BAMEed Network, has been working with schools throughout the pandemic to ensure that the needs of staff from Black and Asian backgrounds in particular, have been adequately taken into account through producing a risk assessment and guidance document specifically for these staff members. Although statistically, Black and Asian colleagues are at higher risk of illness and death from Covid-19, nothing had been produced to safeguard them as frontline workers in schools, in the way that the NHS had accounted for their staff members’ needs as key workers. We were glad to be able to close this gap and produce the guidance for schools ourselves in a timely manner. Part of the guidance document’s purpose was to support schools to do more to see the needs of their staff members that are from Black and Asian heritage, and to start a conversation with them more widely about their lived experience of class, race, and discrimination within our schools, workplaces and society as a whole. The focus on racial justice by the Black Lives Matter movement in the wake of George Floyd’s murder has made this conversation even more relevant and important and it has helped to bring a new lexicon and new understanding of the issues for many, that were oblivious.
It is one thing to consider the importance of racial and social justice on the workplace conditions of adults in our education system, but how do we ensure that this extends beyond ticking boxes of the legal duties of the Equality Act and takes the form of meaningful change over time? Where do we start to ensure that we all improve our awareness and education on these important matters? When is it the right time to start to learn about racial and social justice? One thing that has come to light as a result of the focus on inequities and structural racism endured by Black people and other minoritised people of colour, is that our education system has somehow simultaneously been seeing itself as a great equaliser, while perpetuating structural inequalities through its own practice. Part of the cause for this is the focus on quantifiable, measurable outcomes to come above the more intangible and yet vital ‘soft’ skills of critical thinking, empathy, a sense of collective social responsibility.
It was interesting to see the surge of emotion and the subsequent urgency to take action that ensued from the George Floyd incident and which emulated from the education sector. The BAMEed Network inbox has been inundated with requests for support from every level, be that CEOs of major education organisations, leaders of teacher unions, senior staff at local education authorities, multi-academy trusts or diocesan boards of education, as well as from headteachers and leaders from individual schools, and individuals from within the junior ranks of school staff, or parents, governors and even young people themselves. Across the board, people are looking for answers and seem ready and willing to take steps to ensure that their own practice is inclusive and actively anti-racist.
There’s nothing new here, so what has changed?
Questions of race, racism and teaching are not new and have been debated for decades. One primary site for anti-racist practice is to consider the curriculum. The MacPherson Report, published 6 years after the racially motivated murder of Stephen Lawrence in 1993, strongly suggested that inclusivity and diversity in the curriculum can improve social cohesion, prevent racist attitudes taking hold and instil the value of cultural diversity from an early age in young people. Improvements in the content of the curriculum is vital for many reasons, not least to provide a balanced view of history, and of the contributions of people from a variety of backgrounds who have lived side by side in Britain as the result of migrations from far and wide since the middle ages as well as more recent migrations as a result of our colonial past or the displacement of peoples connected with our involvement in wars in more recent times.
Looking beyond formally taught subject matter, discrimination in education is also enacted through disciplinary practice. For the decades since the MacPherson report recommendation to do so, schools have been dutifully recording racist incidents, monitoring the numbers and self-defined ethnic identity of excluded pupils, and these are published annually on a school-by-school basis. There are a range of practices which underpin Black students’ exclusion and which impact on their educational attainment for example, which are starkly detailed in the DfE Timpson Report on school exclusion of May 2019 and which result in Black British children of Caribbean heritage being more than 1.7 times more likely to be permanently excluded as compared with their white British counterparts.
What seems to have shifted, and potentially divided educators along the way more recently, is the notion of institutional and structural racism which is inherent in every element of society and not least, school life, and which runs like a stick of rock through our practice unless we make particular efforts to seek it out and adjust what we do, accordingly. At the end of the academic year of 2019-20, two major Charter School chains in the USA, Uncommon Schools and KIPP, denounced their own use of ‘carceral’ or ‘no excuses’ discipline techniques as racist. These were practices that had been the cornerstones of their educational philosophy. These techniques have been much lauded by a number of schools in England, and these schools have not subsequently re-evaluated their position, adamant that any less of an iron grip on children’s bodies, gaze and mouths will result in destruction of their lives as disadvantaged young people. The interesting thing is that both camps in this schism around discipline, believe that they are acting in the best interests of the young people from disadvantaged backgrounds that they serve. However, what is clear from one methodology, is that it is about ensuring that young people get the grades, sometimes at any cost, that will take them onto educational pathways for the future without questioning, disrupting or skilling up young people, or their teachers, to see or tackle the socio-political causes for the disadvantage, inequity and structural discrimination which creates such deep divisions in society in the first place – or indeed why the the gap between disadvantaged and non-disadvantaged students has stopped closing. And this is the key dividing line that has seen the initial surge of interest in making changes go through a further self-selection process. After the public statements of intent were posted on websites, or circulated by letters home to parents, some driven by guilt or alarm, and others by an emerging or enduring understanding of racism, it is clear which organisations are willing and able to see that structural racism needs to be dismantled at every level, and which organisations have retreated to tinkering around the edges, at most perhaps creating some better optics and remembering some more pressing issues they might focus on right now. And there are many pressing issues for the education sector right now.
Looking at whether a sharper focus on racial justice in the form of anti-racist practice should be enacted in schools or not is one heck of a question. There are a growing number of programmes, awards, charter marks, organisations, formal change management structures and guide books which are emerging that can support schools to map their pathway to dismantling structural racism in their curriculum, employment and staff development policies and practices, discipline, hair and uniform policies, and in supporting teachers’ professional understanding and practice in the classroom and beyond. However, alongside these developments, there seems to be growing pressure on schools not only to not disrupt the status quo, but with what some educators see as sinister suggestions that doing so may be treading a fine line between enacting the Equality Act and breaking the law for standing up for equality in a way many witnessed during the time of Section 28 only 30 years ago. At the start of the academic year 2020-21, new DfE guidance on the teaching of relationships, sex and health education has become the site of specific instruction to schools around the potentially extreme political stances held by the very resources and external agencies they seek support from to deliver this statutory curriculum area. In this document, such extreme stances include: “divisive or victim narratives” and “selecting and presenting information to make unsubstantiated accusations against state institutions”. Around the same time that this guidance was published, a letter to headteachers and SLT was circulated by a new organisation which sees itself standing up to anti-racist discourse, and specifically Critical Race Theory, as divisive, rife with so-called victim narrative, and potentially illegal, supposedly going against the 1996 Education Act and Teachers’ Standards which state the need for teachers to maintain political neutrality. By shifting the focus in this way, the anti-racism narrative stops being seen as about creating greater race equity, and instead about anti-white sentiment, or is seen as an expression of political leanings rather than a desire to understand the historical and societal causes of inequalities which have played out over generations in terms of educational progression, health outcomes and life-expectancy for Black and Asian British citizens. This group advises teachers that to regard the acceptance of structural racism as fact, to challenge inherent bias, or have any association with Black Lives Matter is politically motivated and therefore should be viewed as indoctrination. In their view, discussion of anti-racism will make teachers, children and their families feel guilt and that actively seeing race is a way to divide us.
What’s the core purpose of education?
When considering whether teaching racial justice and equity has a place in our primary schools, we need to think carefully about the core purpose of education. For the proponents of the ‘no excuses’ education and the charter schools movement, it has been about moving children through the testing process with as much skill and knowledge necessary to ensure that they compete with their more privileged peers and reach the next stage of their education with comparable test scores. Until these tests explicitly contain questions about racial justice and equity, there is no place to learn about it. Our testing system in itself is inherently flawed as it requires one third of children to fail for the two thirds to succeed. In the words of Daniel Koretz in The Testing Charade, “When test scores become the goal of the teaching process, they both lose their value as indicators of educational status and distort the educational process in undesirable ways. That is exactly what happened when high stakes testing became the core of education ‘reform’”.
In modern complex society such as ours, we need to be able to give children something that will serve them as powerful adults with agency in their own right. Learning is as much about agency as it is about knowledge retrieval, and there is a strong body of evidence to suggest that the work that schools do now to prepare their students for the 21st century, should include a consistent and high quality focus on knowledge and understanding, skills and attitudes. Gert Biesta’s work suggests that what we do in the classroom can make the biggest difference to children while they’re in our schools and the way in which we guide them to ‘meet the world’ will serve them now and beyond their schooling. We need to connect education to our core purpose, which cannot simply rest on passing tests.
There are several good examples of schools serving the same kinds of underprivileged cohorts which may receive no excuses, rote-based learning in some circumstances and yet which deploy an entirely different framework for learning and discipline. School 21 in Newham for example, is an all-through school which educates the ‘head, heart and hand’, seeing the aim of school to educate for knowledge, values and attitudes and also manual skilled tasks such as craft and handiwork. Inherent in their curriculum will be what they call ‘Real World Learning’ about social justice, and developing the critical skills to know, think and to talk coherently about history, politics, societal structures, inequalities and more. Students are engaged in answering complex questions in partnership with organisations such as the Justice Department and the Metropolitan Police, such as ‘With the continual restrictions on legal aid, how can we ensure wide-ranging and fair access to justice?’ and ‘Does the Met Police effectively engage with young people and what could we do differently?’
At primary, Inspire Partnership Trust serves disadvantaged areas Greenwich, Medway and Croydon. Their curriculum structures itself around similar lines to School 21 with a focus on the cognitive (head), affective (heart) and psychomotor (hand) domains of learning. Academic engagement is rooted in relationships, and is about students’ own commitment to being a learner, social engagement as an active participant in school life and intellectual engagement in the learning. The curriculum framework is rooted in core texts which have been carefully selected to be contemporary enough to allow pupils to engage deeply and critically with a range of complex issues, linking to an outcome which has a social justice element and supports children to make sense of a modern complex society with strong and robust knowledge which will help them develop the skills they need to navigate some of the challenges they will encounter in life. For both these examples, the journey of learning is what makes the outcome strong and there is absolutely a place to give the children the knowledge they need to understand the past, the present and to imagine a more just and equitable future, which they will be active agents in creating. In this way, providing children a way to make sense of themselves as learners, a focus on themselves as meeting the world but not the centre of the world, gives them and their teachers the opportunities to be trusted to explore complex societal problems such as inequity, race and racism, gender, climate change and more. Schools like these should and absolutely do see themselves as equipped and adept at teaching racial justice and equity, without fear of straying from their core purpose. In the words of Paulo Friere, “Education is a political act. No pedagogy is neutral… Knowledge emerges only through invention and re-invention, through the restless, impatient, continuing, hopeful inquiry human beings pursue in the world, with the world and with each other.” And so it stands that while racial injustice and inequity exist in the world, so must learning to dismantle them exist in the education of both teacher and student.